Brexit
UK customs law is changing and will continue to evolve
European Union is a customs union, which means there is no border control and a common external tariff is applied to all goods entering the union. No customs duty is applied when goods move between member states. This applies to all the goods including imported goods, on which duty is paid initially by a member state and released by customs as free circulation goods. UK joined EU in 1973 and left in 2020. UK is no longer part of EU’s Customs territory. In rundown, the accompanying changes have produced results since 1 January 2021.
- New customs, VAT and excise legislation introduced to cover exports and imports to EU and ROW.
- NI Protocol in place to avoid hard border on island of Ireland, unfettered access to UK internal market for NI businesses, avoid tariffs on goods moving between GB and NI, and determine goods ‘at risk’ of entering EU.
- EU-GB imports subject to 6 months phased approach on SPS checks, customs controls and declarations.
- UK-EU Trade and Cooperation Agreement secured for tariff and quota free trade between UK and EU-EU-GB imports subject to 6 months phased approach on SPS checks, customs controls and declarations
- UK Global Tariff confirms new rates of duty for all imports
- Introduction of Postponed Import VAT Accounting
- UK joins Common Transit Convention
Following the UK’s take-off from the EU, components of existing legislation will be held however corrected after some time to mirror the UK’s advancing improvement of global exchange.
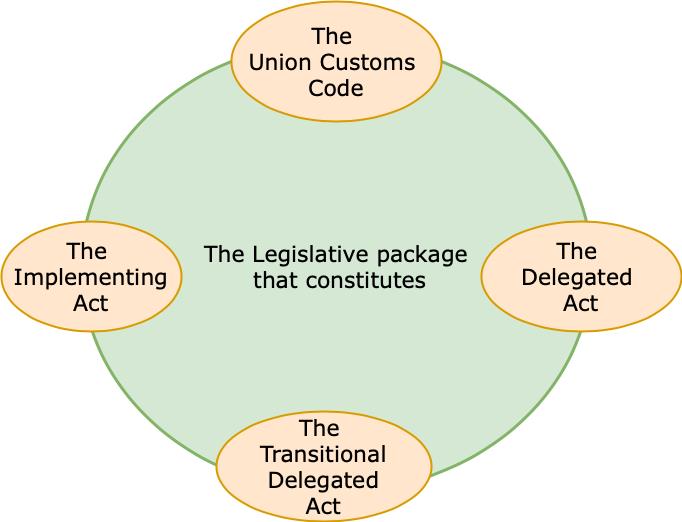
“The Union Customs Code” requires data to be submitted to Customs authority before entry or exit of goods at port, “The Delegated Act” explained WHAT(the list of data element to be submitted) and “The Implementing Act” explained HOW(the way needs to be submitted).
TDA is a transitional arrangement for the members states where UCC IT work programme is not fully functional, Article 278 of UCC allows paper-based method where the required IT system is not available( until 31 Dec 2020)
Union Customs
Treaty of Lisbon is signed on 13 December 2007 and became effective in 2009, more powers were given to EU under this treaty. This treaty also clearly identify powers between EU and its member states. It introduces new rules and concepts for the adaption of legislative act such as UCC and introduction to implementing rules. There are two treaties resulted in the two primary Lisbon Treaties of the European Union:
- The Treaty on European Union (TEU).
- The Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU).
- For the adoption of legislation in the EU, the TFEU sets the rules and the way in which the rules have been set results in the need for four different acts relating to Customs that must be read in conjunction with each other.
List of EU Member States : Following is the list of the member states; In the order, they have joined the union (UK joined EU in 1973 and left in 2020).




















Member States of the Customs Union are :
All 27 EU member states + Turkey, Andorra and San Marino ( UK is no longer part of EU’s Customs territory).
Member States of the European Free Trade Association(EFTA) are :
Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
Member States of the European Economic Area (EEA) Agreement are :
Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway.
Union and Non-Union Goods
Union Goods include:
- Goods which are wholly obtained in the customs territory of the Community EU that don’t incorporate goods imported from external countries or territories
- Goods which are imported from countries or territories that don’t form part of the customs territory of the Community EU which have been released for free circulation
- Goods obtained or produced in the customs territory of the Community EU that incorporate other Union goods
All other goods have the status of non-Union Goods, and as such are not in free circulation.